The cyberattack landscape predictions for this coming year are coming in. This time, cybercriminals are expected to up the ante making attacks like ransomware more sophisticated and effective—with AI making all attacks real wild cards.
Organizations are preparing for this year’s crop of escalated cyberattacks, and new regulations will also present a challenge for their systems. But criminals won’t stop their attacks, so keeping on top of the risks is your best bet.
CIRCIA Upfront
There’s a new law affecting all organizations who are victims of cybercrime in the U.S. Due to take effect soon is a law known as CIRCIA, or the Cyber Incident Reporting for Critical Infrastructure Act of 2022. Through required reporting, CIRCIA promotes transparency and accountability for businesses when cybercrimes occur. It also allows CISA (Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency) to identify attack trends and share that information with those benefiting from it. CISA can also use CIRCIA information to quickly help victims of attacks.

Generative AI, or GenAI (think ChatGPT)
AI continues to grow. In particular, social engineering attacks benefit from its use. With a few key words, cybercriminals can plot pointed phishing attacks on a massive scale without displaying the usual red flags of phishing like poor spelling and grammar. Deepfakes and voice cloning are other GenAI areas ripe for the picking. Overall, GenAI will make phishing and other social engineering attacks more convincing.
Ransomware
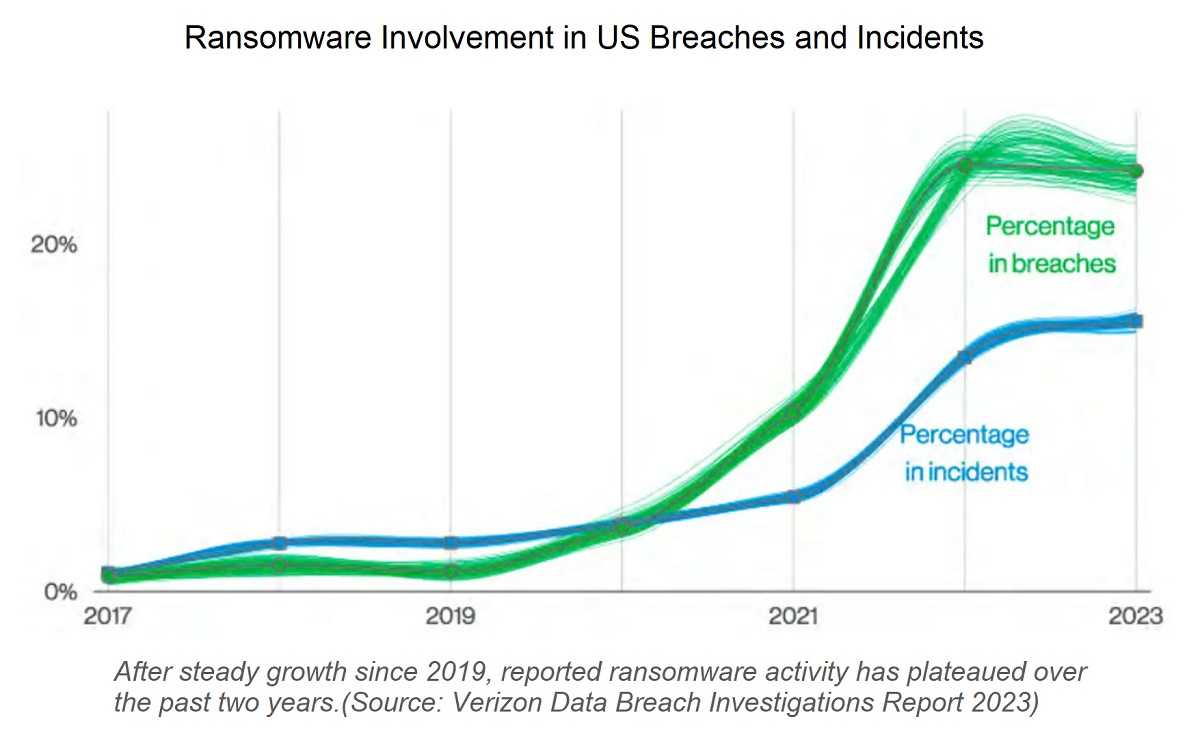
This is considered the scourge of healthcare, education, businesses, and state and city services (to name a few). Ransomware is all about cybercriminals getting ransom payments for critical data they’ve encrypted. Adding to this attack is double extortion against ransomware victims using their hijacked sensitive data. According to Verizon, ransomware was involved in 24% of all data breaches last year.
Hacking as a business is booming
With Malware as a Service (MaaS) available to rent or buy on the dark web, hackers have all they need for their cyberattack goals. Attacks by aspiring hackers and their rented malware of choice have it easy with tutorials and step-by-step instructions. Also, “hired guns” are available to do your hacking for you. It’s believed more threat groups will offer hacking as a service for the right price.
Cyber-education and Zero Trust
These are two practices businesses need more of this year. With 96% of malware delivered via email, employees of every level from bottom to top benefit from recurring cybersecurity awareness training. Zero trust for organizations means no one is trusted by default. Whether inside or outside an organization’s network, as with employees and vendors, verification is required every step of the way with system interaction.
What you can do
Always have your guard up for various attacks. Consider a zero-trust policy for yourself when it comes to providing sensitive information to anyone. Make sure the person on the other end of the phone is really who they claim to be and hold that information close until you’re sure. Pay attention to email and text messages, as well as visual voice messages. If you cannot be sure, double check. Keep all of your systems updated and install anti-virus/anti-malware software on every one of them.
Want to know more? Read additional Mid Oregon blog articles about online security and fraud protection.
As a reminder, Mid Oregon will never initiate a call asking for personal or account information via phone, text, or email.
Content based on an article by Stickley on Security





